
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is changing the way healthcare works. From faster diagnosis to better patient care, AI is helping doctors and hospitals make smarter decisions. Instead of replacing healthcare professionals, AI supports them by making everyday tasks easier and more accurate. Whether it’s predicting disease risk, organizing patient data, or helping with treatment plans, AI is proving to be a powerful tool in modern medicine. As healthcare systems around the world face growing challenges, including rising costs and a need for faster services, AI is offering real solutions that improve both patient outcomes and hospital efficiency.
How AI is Leveraged in Healthcare
AI is being used in many parts of healthcare to improve how services are delivered. One key area is diagnosis. AI tools can quickly analyze medical images such as X-rays and MRIs, helping doctors detect issues like tumors or fractures with greater accuracy. This speeds up the diagnostic process and reduces the chances of human error.
In patient care, AI helps monitor vital signs in real-time, alerting staff to changes that may need urgent attention. This kind of early warning system can be life-saving in emergency situations.
AI also plays a big role in administrative tasks. Hospitals use AI to manage patient records, schedule appointments, and even assist in billing. This cuts down on paperwork and gives healthcare staff more time to focus on patients.
Another growing use is in personalized treatment. AI can study a patient’s history, genetics, and lifestyle to help doctors create custom treatment plans. This makes care more effective and specific to each patient.
By combining speed, data analysis, and accuracy, AI is becoming a reliable partner in the healthcare journey—helping medical teams deliver better care to more people.
Top Benefits of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
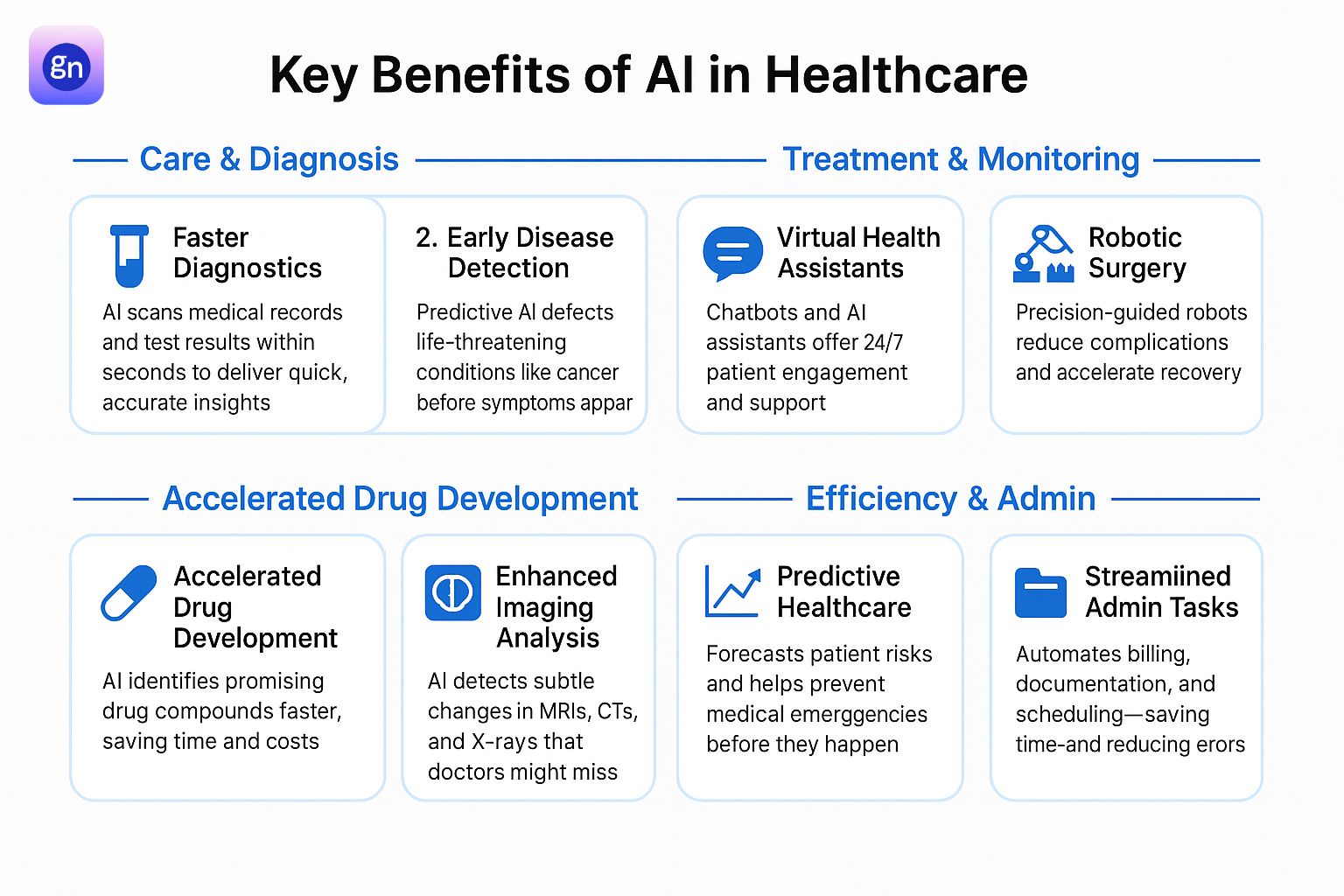
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming every layer of the healthcare system—streamlining operations, supporting faster diagnosis, and enabling more personalized and proactive care. Below are the most impactful and specific benefits of AI across healthcare domains:
1. Drug Development
AI accelerates the drug discovery process by predicting how different molecules will interact with biological targets. Traditional drug development takes over a decade and costs billions, but AI-powered models can identify promising drug candidates in a matter of weeks by analyzing complex chemical and genomic data.
AI algorithms use existing medical databases and real-world evidence to simulate how new drugs may perform in clinical trials. This helps pharmaceutical companies eliminate compounds with low success potential early, saving time and resources. Moreover, AI assists in optimizing trial designs, selecting the right patient cohorts, and predicting possible adverse reactions based on biological markers.
2. Patient Engagement
AI enhances patient engagement through interactive platforms such as virtual healthcare assistants and conversational bots. These tools provide patients with 24/7 support—answering common health-related queries, reminding them about medications, and guiding them through pre- and post-treatment care instructions.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables AI systems to understand and respond to patient concerns in a human-like manner, improving satisfaction and health literacy. Personalized health apps powered by AI track user behaviors and provide insights or nudges to encourage lifestyle changes, making patients more active participants in their care journey.
3. Enhanced Patient Care
AI-driven decision support systems help clinicians by providing evidence-based recommendations at the point of care. These tools analyze patient histories, current symptoms, and clinical guidelines to suggest optimal treatment pathways. This reduces variability in care, ensures adherence to best practices, and enhances overall quality.
For example, AI can flag abnormal lab results or subtle trends in a patient’s health records that might otherwise go unnoticed. It can also help prioritize care for high-risk patients, ensuring timely interventions. The result is more efficient, accurate, and personalized patient care.
4. Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
AI-enabled RPM systems use wearable devices and sensors to track vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, glucose levels, and oxygen saturation in real-time. This data is processed through machine learning models that detect anomalies and generate alerts when medical intervention may be needed.
By enabling continuous, real-time monitoring outside clinical settings, AI reduces unnecessary hospital visits and allows for early detection of health deteriorations. This is particularly valuable for managing chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and heart failure, where consistent monitoring significantly impacts patient outcomes.
5. Imaging Analysis
AI has revolutionized medical imaging by drastically improving image interpretation speed and precision. Machine learning models trained on vast datasets can identify abnormalities in X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds with high accuracy—sometimes surpassing human radiologists in early-stage detection.
For instance, AI is widely used to detect lung nodules, brain tumors, and diabetic retinopathy. It not only highlights potential problem areas for the radiologist’s review but can also quantify lesion size, growth rate, and likelihood of malignancy. This reduces diagnostic turnaround times and helps in making informed clinical decisions swiftly.
6. Drug Creation
Beyond development, AI is increasingly used in drug design and synthesis. Generative AI models can create novel molecular structures tailored to specific biological targets. These models simulate how a molecule will behave, interact, and metabolize inside the human body.
AI also helps optimize the chemical structure of potential drugs to improve stability, bioavailability, and safety profiles. Pharmaceutical companies are integrating AI with lab automation and robotics to test compounds at scale, turning AI from a theoretical tool into a production engine for new medicines.
7. Personalized Medicine
AI enables the shift from one-size-fits-all care to truly personalized medicine. By analyzing data from electronic health records, genetic profiles, lifestyle habits, and previous treatment responses, AI models can recommend therapies tailored to individual patients.
This approach is especially impactful in oncology, where treatment options can vary widely depending on tumor type, mutation status, and patient biology. AI can predict how a specific patient will respond to chemotherapy or immunotherapy and recommend the most effective and least harmful treatment.
Personalized medicine supported by AI leads to improved outcomes, fewer side effects, and more efficient use of healthcare resources.
8. Improved Diagnostic Accuracy
AI enhances diagnostic accuracy by combining clinical expertise with computational precision. It cross-references symptoms, lab reports, imaging data, and historical cases to provide differential diagnoses with high confidence levels.
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) powered by AI help identify rare or complex diseases that might be missed in a routine exam. For example, in dermatology, AI can differentiate between benign and malignant skin lesions with remarkable accuracy using dermatoscopic images.
Reducing diagnostic errors means better patient outcomes, reduced malpractice risk, and optimized treatment plans from the start.
9. Improved Healthcare Access
AI helps bridge healthcare access gaps in underserved or remote areas. Virtual health assistants and AI-powered telehealth platforms provide initial consultations, triage support, and medical guidance to patients without the need for a physical clinic visit.
Mobile diagnostic tools embedded with AI can operate in low-resource settings, offering automated analysis of blood samples, retinal scans, or chest X-rays. This empowers community health workers to make timely decisions and escalate serious cases to higher levels of care when needed.
By extending the reach of medical services, AI contributes to more equitable and inclusive healthcare systems.
10. Medical Imaging
In medical imaging, AI is not only assisting in interpretation but also in image enhancement and workflow optimization. AI algorithms can improve image clarity, remove noise, and reconstruct low-quality scans, allowing for better analysis even with minimal radiation exposure or limited imaging resources.
AI also assists in automated image segmentation, identifying organs and structures with precision, which is vital for pre-surgical planning, cancer staging, and radiation therapy targeting.
Moreover, AI streamlines radiology workflows by automatically sorting studies, flagging critical cases, and generating preliminary reports. This allows radiologists to focus on complex cases and reduces report turnaround time.
11. Robotic Surgery
AI-powered robotic systems are enhancing surgical precision and outcomes. These systems assist surgeons during complex procedures by providing 3D visualization, real-time guidance, and stability beyond human capabilities. For example, AI-integrated robotic arms can make micro-movements with minimal margin for error, reducing the risk of tissue damage.
Machine learning models are also used to analyze past surgical data to suggest optimal approaches based on patient-specific factors. With robotic assistance, surgeries become less invasive, recovery times are shorter, and the overall surgical experience is safer for patients.
12. Clinical Trials
AI accelerates the clinical trial process by optimizing patient recruitment and predicting trial success. Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools can sift through millions of electronic health records to identify eligible candidates based on inclusion/exclusion criteria, demographics, and biomarkers.
Moreover, AI helps in adaptive trial designs, where algorithms analyze ongoing results and adjust protocols in real-time for better efficiency. By forecasting patient responses and identifying adverse events early, AI contributes to more effective and faster drug development.
13. Early Disease Detection
Early detection is crucial for effective treatment and improved survival rates. AI systems are trained to identify subtle patterns in lab results, imaging scans, and genetic data that may indicate the onset of diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer’s, or cardiovascular conditions—often before symptoms appear.
For example, AI can analyze retinal scans to detect early signs of diabetic retinopathy or scan lung images to flag precancerous nodules. The earlier a disease is caught, the better the prognosis and treatment options available.
14. Fast Diagnostics
AI speeds up diagnostic workflows by quickly analyzing large datasets and medical images. In pathology, radiology, and dermatology, AI models are used to detect abnormalities such as tumors, lesions, or fractures with high sensitivity and specificity.
This acceleration allows healthcare providers to act quickly, particularly in emergency settings where time is critical. AI tools can produce preliminary diagnostic reports in minutes, allowing clinicians to prioritize care for patients needing immediate attention.
15. Virtual Health Assistants
Virtual health assistants use AI and conversational interfaces to support patient communication and care management. These tools answer questions, book appointments, provide medication reminders, and deliver post-discharge instructions—all without requiring human intervention.
More advanced assistants are capable of symptom checking and triaging based on basic information provided by the patient. This improves patient engagement and provides 24/7 support, especially in primary care and chronic disease management.
16. Automation
AI is streamlining a wide range of repetitive tasks in healthcare—from billing and coding to lab result documentation. Intelligent automation tools can extract information from medical records, categorize it appropriately, and input it into hospital systems, reducing manual workload.
By freeing up clinicians and administrative staff from time-consuming tasks, AI allows them to focus on patient-centered activities, improving both operational efficiency and care quality.
17. Better Preventive Care
Preventive healthcare is moving from a reactive model to a predictive one, thanks to AI. By analyzing lifestyle data, genetics, wearable device output, and medical history, AI can identify at-risk individuals and recommend timely interventions.
For instance, predictive algorithms can warn patients about rising blood pressure or detect irregular heart rhythms before they develop into major issues. This allows physicians to initiate preventive measures like lifestyle counseling or medication adjustments, ultimately reducing hospital admissions.
18. Personalized Treatment Plans
AI tailors treatment recommendations to the unique characteristics of each patient, taking into account their genetics, environment, comorbidities, and response to past treatments. This is particularly valuable in oncology, where AI helps match patients with targeted therapies based on tumor genetics and molecular profiling.
AI also supports dosing optimization, predicting how a patient might metabolize a drug, and adjusting dosage accordingly to reduce side effects and increase effectiveness. Personalized care driven by AI leads to better health outcomes and higher patient satisfaction.
19. Enhanced Accuracy
In clinical environments, AI improves accuracy in both diagnosis and treatment delivery. Algorithms trained on vast medical datasets can recognize inconsistencies or anomalies that may be missed by the human eye, helping reduce misdiagnosis and treatment errors.
In radiation therapy, for instance, AI ensures that the treatment is delivered to the exact target area, minimizing damage to healthy tissues. Similarly, AI in anesthesia management can continuously adjust dosages for optimal sedation during surgery based on patient vitals.
20. Predictive Healthcare
Predictive healthcare focuses on anticipating medical events before they occur. AI models evaluate historical data, lab results, lifestyle factors, and real-time monitoring to forecast events like hospital readmission, disease relapse, or acute episodes.
Hospitals can use this predictive analytics capability to implement proactive care strategies, allocate resources efficiently, and improve patient outcomes. For example, AI can alert care teams about a patient’s risk of sepsis, enabling early intervention and potentially saving lives.
21. Streamlined Administrative Tasks
Administrative burden is a known contributor to clinician burnout. AI reduces this burden by automating tasks such as medical transcription, insurance claims processing, patient intake documentation, and compliance reporting.
Voice recognition tools and NLP-based documentation assistants help clinicians record patient notes more quickly and accurately. AI also organizes patient files and flags missing or inconsistent data, making information retrieval seamless and reliable.
22. Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics enables healthcare organizations to make data-backed strategic decisions. Hospitals can use AI to forecast patient admissions, optimize staffing levels, manage supply chains, and reduce operational bottlenecks.
On a patient level, predictive analytics assists in population health management. AI can segment patient populations based on risk levels, enabling tailored outreach programs and targeted interventions for chronic disease management.
23. Accurate Diagnosis
AI supports diagnostic precision by integrating and interpreting diverse data sources. From imaging and lab reports to genetic tests and EHRs, AI synthesizes this information to offer diagnostic suggestions that are evidence-based and often faster than traditional methods.
This is especially useful in areas like rare diseases or complex conditions, where traditional diagnosis can take years. AI can detect overlooked patterns, leading to faster identification and treatment.
The Role of AI in Reducing Errors and Improving Accuracy
One of AI’s most transformative contributions to healthcare is its ability to minimize human error and enhance diagnostic and procedural accuracy. Medical errors—whether in diagnosis, documentation, or treatment—can have life-altering consequences. AI-powered systems, trained on vast clinical datasets, can cross-reference symptoms, lab results, imaging, and patient histories to detect inconsistencies and flag anomalies that might be overlooked by human practitioners.
In radiology, AI algorithms assist in identifying tumors, fractures, or organ abnormalities with high sensitivity and specificity. In pathology, they can highlight mislabelled samples or suggest second opinions. AI also ensures dosing precision in treatments like chemotherapy or anesthesia based on real-time patient data.
By functioning as a second layer of analysis, AI reduces diagnostic oversights and streamlines decision-making. When used responsibly alongside human expertise, AI tools significantly increase the reliability and safety of healthcare delivery.
Bridging the Gap Between AI and Human Intelligence
AI is a powerful ally, not a replacement, for human intelligence in healthcare. While AI excels at processing large volumes of structured and unstructured data, it lacks the emotional intelligence, ethical reasoning, and contextual awareness that human clinicians bring to patient care. Bridging the gap between AI and human expertise involves creating symbiotic workflows where machines handle repetitive, data-heavy tasks and clinicians focus on nuanced decision-making and compassionate care.
Effective integration requires intuitive interfaces, explainable AI models, and continuous feedback from healthcare professionals to refine algorithm performance. Clinical validation and regulatory oversight further ensure that AI recommendations are safe and reliable.
This collaboration empowers doctors to make better-informed decisions, reduce cognitive overload, and spend more quality time with patients. When AI augments rather than replaces human skill, it enhances overall care quality and leads to more holistic, patient-centered outcomes.
Harnessing AI for a Healthier Future
As healthcare systems face growing demands, AI offers scalable solutions to support a healthier future. From rural telemedicine to personalized cancer treatments, AI ensures care is timely, accessible, and tailored to individual needs. Predictive models help identify disease trends, manage resources, and anticipate patient needs before they escalate—shifting care from reactive to proactive.
In public health, AI enables early detection of outbreaks and optimizes vaccination strategies through real-time data analysis. In clinical research, it accelerates discoveries by finding patterns across millions of datasets that the human brain could not process alone.
However, the path forward must prioritize ethical deployment, patient data privacy, and equitable access to AI-driven tools. Investments in AI literacy, infrastructure, and cross-disciplinary collaboration are essential.
By responsibly harnessing AI, the healthcare industry can build systems that are smarter, faster, and more compassionate—delivering better outcomes for individuals and communities worldwide.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is not just transforming healthcare—it’s redefining it. From enhancing diagnostic accuracy and accelerating drug development to enabling personalized treatments and streamlining clinical workflows, AI is solving long-standing challenges with speed and precision. Its ability to learn from vast datasets and assist healthcare professionals in making informed, data-driven decisions is already improving outcomes for patients and providers alike.
However, the true potential of AI lies in its thoughtful integration—with transparency, human oversight, and patient trust at the center. As we continue to harness AI technologies, it’s essential to ensure ethical standards, data privacy, and equitable access across all populations.
At GlobalNodes, we believe AI is the foundation for a more intelligent, connected, and proactive healthcare system. By embracing innovation responsibly, we’re not just building better tools—we’re helping build a healthier future for all.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the advantage of artificial intelligence in health care?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) enhances healthcare by improving diagnostic accuracy, enabling faster decision-making, and reducing administrative burdens. AI systems can analyze medical images, lab results, and patient records with speed and precision, helping clinicians detect diseases earlier and more accurately. Additionally, AI supports personalized treatment plans and streamlines hospital workflows, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and more efficient care delivery.
2. What are the advantages and benefits of using AI in healthcare?
AI offers multiple benefits across the healthcare spectrum:
- Faster diagnostics through data-driven insights
- Enhanced patient engagement via virtual assistants and AI chatbots
- Reduced errors in diagnosis, medication, and surgery
- Remote patient monitoring for chronic condition management
- Personalized treatments based on genetic and lifestyle data
- Automation of administrative tasks, allowing healthcare staff to focus more on patient care
- Predictive analytics for early disease detection and preventive care
These benefits collectively improve the efficiency, accessibility, and quality of healthcare services.
3. What are the applications of artificial intelligence in healthcare?
AI is used in various healthcare domains, including:
- Medical imaging for tumor detection and disease diagnosis
- Robotic surgery for enhanced precision and reduced recovery time
- Drug development by identifying compounds and predicting success rates
- Clinical trials optimization through AI-driven patient selection and monitoring
- Virtual health assistants for symptom checking and patient communication
- Predictive healthcare models to anticipate epidemics and health risks
- Administrative automation for billing, scheduling, and medical coding
These applications contribute to more responsive, accurate, and data-informed healthcare systems.
4. What are the future uses of AI in healthcare?
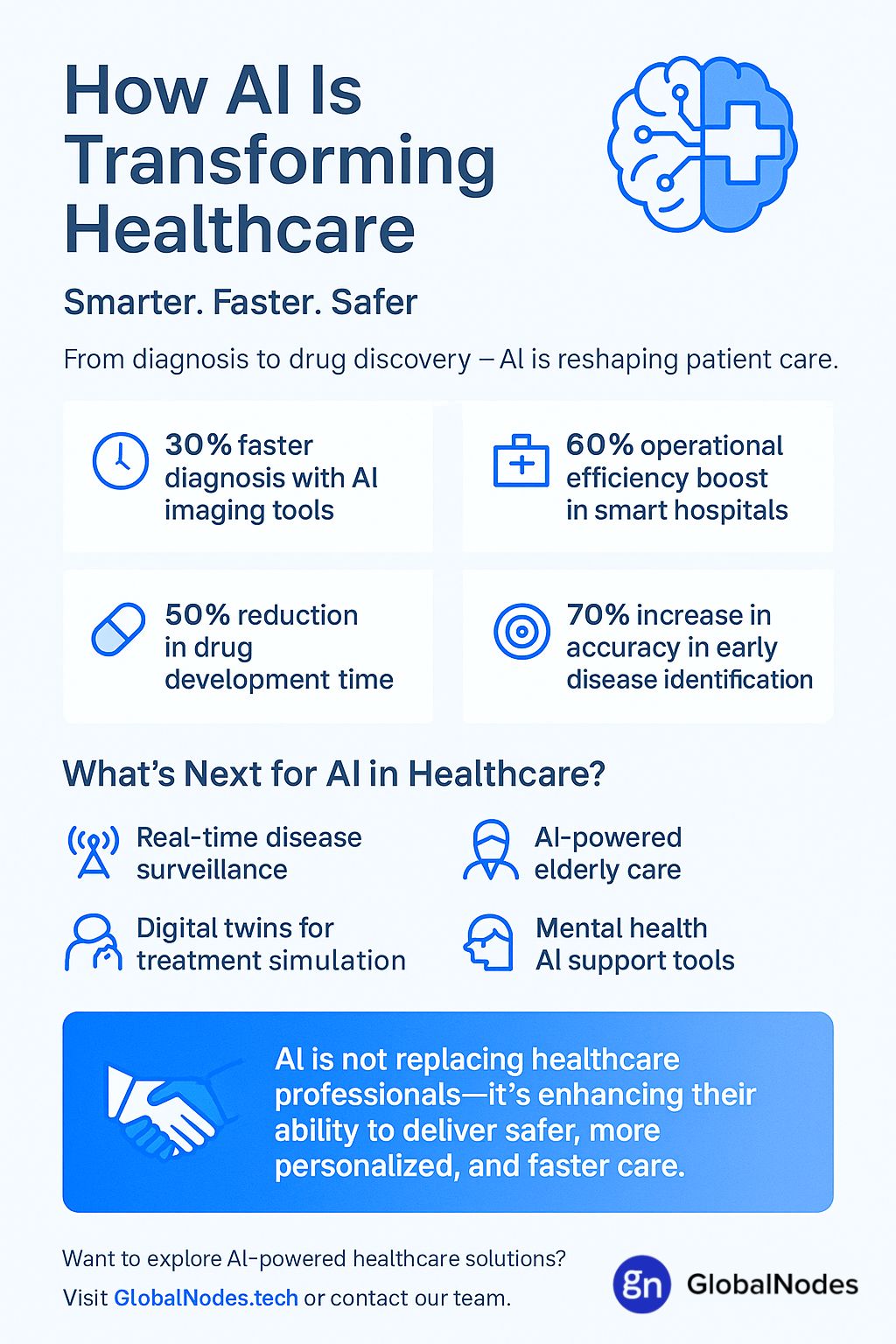
The future of AI in healthcare is promising and rapidly evolving. Key upcoming uses include:
- Real-time diagnostics through wearable health devices
- Genomic AI to customize treatment at the DNA level
- AI-powered mental health support using NLP and behavioral analysis
- Augmented diagnostics that continuously learn from global datasets
- Fully autonomous AI triage systems in emergency and remote settings
- AI in elder care to monitor health and provide companionship
- Digital twins of patients for virtual simulations of treatment plans
As technology matures, AI will continue to redefine preventive care, patient engagement, and personalized medicine.





